In the evolving world of precast concrete, making the right design decisions is crucial for the success of any project, especially when it comes to large-scale infrastructure like multi-story parking buildings. The choice between different types of precast slabs—such as hollow-core and double-tee—can significantly impact the performance, cost, and construction time of a project. In this insightful discussion, Prashant from StruEngineers India Pvt. Ltd. and senior structural engineer Mangesh Dhumal delve into the technical intricacies of choosing the best precast slab for parking structures, focusing on the practical applications, challenges, and advantages of each option.
Prashant: Friends, welcome to the exciting world of precast concrete! I’m Prashant from StruEngineers India Pvt. Ltd., and we are in the business of structural design for precast elements and structures. You might have followed us on LinkedIn or seen some of our posts related to various case studies or technical topics. This time, we thought we’d do a video instead of an elaborate technical post to discuss the technical aspects that go into designing a precast structure.
We have done a lot of case studies—data centers, high-rise buildings, residential buildings, schools, parking terminals, and more—but what really makes a particular precast building successful is the design aspect. Today, we have with us my colleague Mangesh. Hi, Mangesh!
Mangesh: Hi, Prashant. It’s a pleasure to be here.
Prashant: Same here. So, Mangesh, we’ve been talking about case studies, and I think we have showcased a lot of them. But today, I thought we could dive into the design intricacies of what exactly goes on behind the scenes. Whether it’s a conventional structure or a precast structure, the design is what makes the structure successful and fulfills the utility expected of it. I’ve seen you design many different kinds of structures, like data centers and parking terminals. How about discussing the intricacies of designing a multi-story parking building today?
Mangesh: That’s great! Parking structures are dynamic and require careful and meticulous study. We need to understand the force path through the structure.
Prashant: Exactly. Most people watching this are likely aware of what precast is and the benefits it offers. For a parking building, the expectation is usually that the structure should be ready as soon as possible so that people can start using it. Precast is ideal for this. But when it comes to a precast parking structure, I’ve seen two distinct possibilities—hollow-core slabs and double-tee slabs. What differentiates the choice? What makes you choose a hollow-core slab for a parking building and a double-tee slab for another?
Mangesh: That’s a nice technical question. It’s quite simple, really. A slab transfers the load to the beam, the beam carries the load to the column, and the column to the foundation. That’s the basic function of a slab. However, the choice depends on the structural shape. A hollow-core slab has many holes in it and is pre-stressed, while a double-tee slab has a web portion and a flange portion. Both pre-stressed slabs have their pros and cons.
When designing a parking structure, there are certain factors we need to consider. First, the load is very high, and it’s moving. Secondly, if it’s a precast structure, the elements need to be carried by a crane, so crane capacity comes into play. If we go for cast-in-place structures, the section depths increase, so we opt for pre-stressed elements. Hollow-core slabs have holes that make them lighter, making it easier for cranes to erect them.
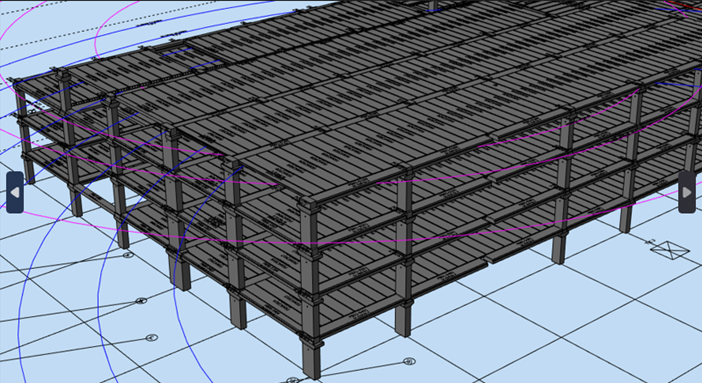
Car parking with Hollow core slabs
Prashant: So, the hollow-core slab is preferred for its lightness due to the holes. But does this also affect the load-carrying capacity? If I compare a double-tee slab with a hollow-core slab, does the hollow-core slab have a lesser weight-carrying capacity? What happens if double-tee slabs aren’t available?
Mangesh: That’s a good point. Hollow-core slabs are more commonly manufactured because they are simpler to produce, and the molds are readily available. However, double-tee slabs have a web portion with specific thicknesses and particulars, making them less common. Hollow-core slabs are easier to manufacture and transport, which affects cost.
For example, when we design a parking structure, we need to consider the load distribution. If the structure includes ramps, the center of gravity shifts, placing more load on the front wheels of vehicles, which can cause the hollow-core slab to crush. To prevent this, we can fill the holes with concrete, but this must be done on-site, which isn’t always practical.
On the other hand, double-tee slabs provide a simpler and more effective load transfer, as the force moves directly from the slab to the beam and then to the column. This makes double-tee slabs a better choice for longer spans and heavier loads.
Prashant: That makes sense. So, if you’re not filling the hollow-core slab holes with concrete, it’s not recommended for ramps due to potential issues with load distribution and center of gravity. Double-tee slabs seem more reliable for heavier vehicles and larger spans. But what if double-tee slabs aren’t available? Do people go for cast-in-place waffle slabs or post-tensioned slabs?
Mangesh: Yes, that’s true. If double-tee slabs aren’t available, many opt for cast-in-place waffle slabs or post-tensioned slabs. However, this affects the timeline for completing the structure. The benefit of precast is the reduced time needed for construction, which is crucial when you’re trying to meet tight deadlines.
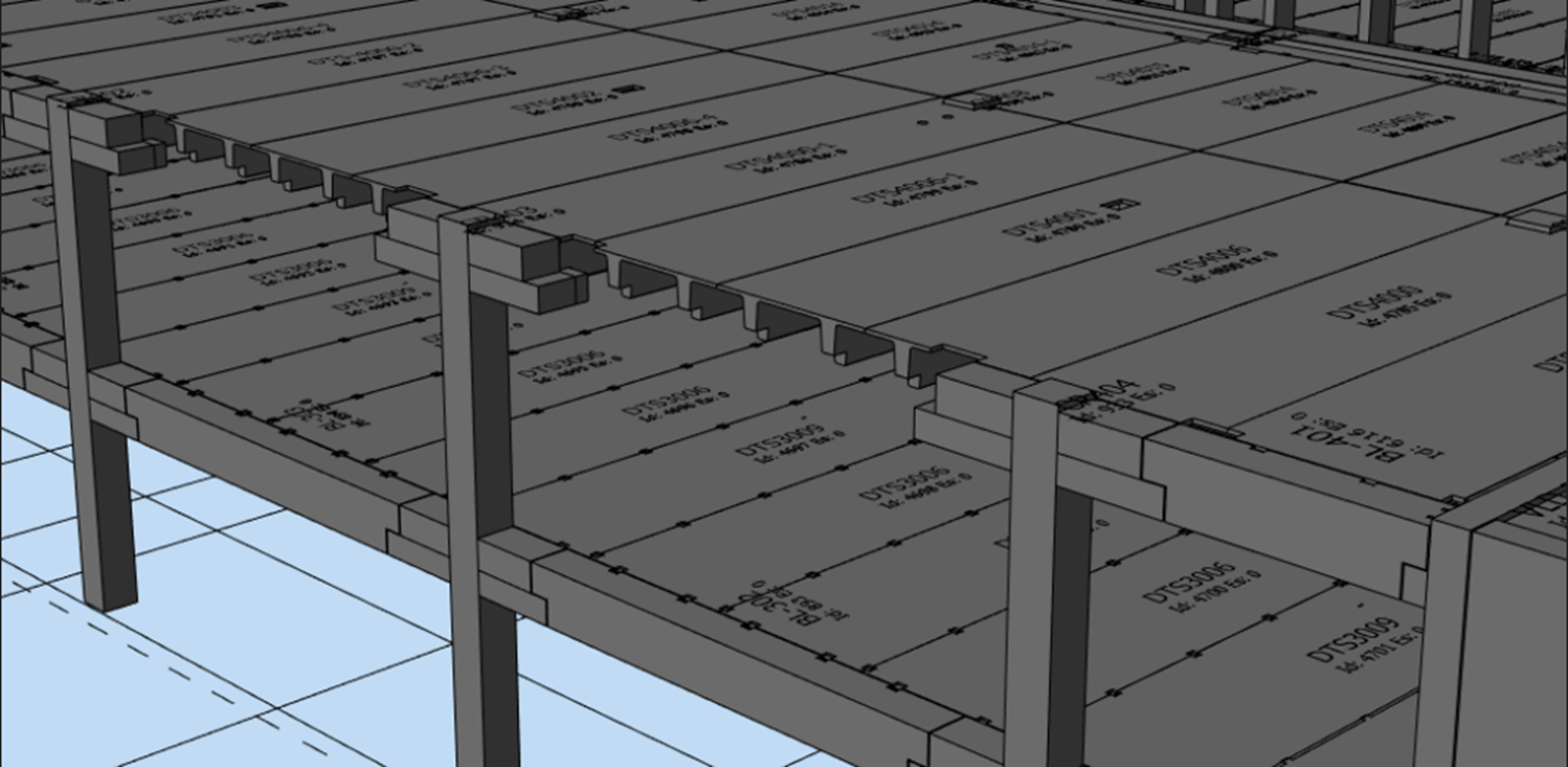
Car parking building with Double Tee slab
Prashant: So, the plus point of using more precast elements and less cast-in-place work is that it saves time, allowing the project to be completed on schedule. That’s essential for keeping costs down and meeting deadlines. But what about seismic considerations? I’ve heard that precast structures aren’t ideal for seismic regions.
Mangesh: That’s a common concern, but there are solutions. Countries like the U.S. and New Zealand, which are prone to seismic activity, use precast structures with emulative joints. These joints are filled on-site, creating a more homogeneous structure that behaves like a conventional cast-in-place structure. However, this requires a thorough seismic analysis to ensure the structure can withstand lateral forces.
Prashant: This has been an interesting comparison. If you had both types of slabs available for a parking structure designed to hold 2,000 cars, what factors would you consider before choosing which slab to use?
Mangesh: The key factors would be availability, cost, and technical considerations. We would evaluate the loading conditions, spans required, and the overall design efficiency. A thorough 2D analysis would be followed by 3D simulations to ensure the design meets all the necessary codes and provisions. The final choice would depend on balancing practicality and cost-effectiveness.
Prashant: Thanks for the detailed explanation, Mangesh. It’s clear that the choice between hollow-core and double-tee slabs involves multiple considerations, from load distribution to cost and availability. I think this discussion will be valuable for anyone involved in designing precast parking structures.
Mangesh: It was a pleasure discussing this topic. Thank you, Prashant.
Prashant: So, friends, today we explored the differences between hollow-core and double-tee slabs for parking structures, especially for multi-story parking buildings. Mangesh explained the factors that go into choosing the right elements for any precast structure clearly. We look forward to having more such technical discussions. Thank you for your time.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Precast Slab Selection
As we’ve explored in this discussion, the choice between hollow-core and double-tee slabs is not just a matter of preference but a decision that can influence the entire structure’s functionality and efficiency. Whether it’s the load-bearing capacity, the ease of installation, or the adaptability to architectural demands, each slab type brings its own set of advantages and challenges. Mangesh’s expertise highlights the importance of careful consideration and analysis in making these decisions, ensuring that the final choice aligns with the project’s specific requirements.
For companies in the UK and Ireland looking to optimize their parking building projects, StruEngineers offers unparalleled expertise in precast concrete design. Our team is equipped to guide you through these complex decisions, ensuring your structures are not only cost-effective but also durable and efficient. We invite you to watch the full discussion below to gain deeper insights into the world of precast slab selection.
You can watch the full discussion below: